In Ireland, domestic abuse is still a major problem, but one type that’s often overlooked is also one of the most insidious. Elder Abuse.
Older people can suffer abuse by their adult children, or other people they come into contact with.
According to a 2014 report by the HSE Elder Abuse Service, of the reported cases of elder abuse:
• 83% happened in the victim’s home.
• 7% in a private nursing home.
• 4% in a relative’s home.
• 4% in public continuing care.
But what is Elder Abuse?
There are many types of elder abuse, which may result from deliberate intent, neglect, thoughtlessness or ignorance.
Elder Abuse has been defined as a single or repeated act, or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any relationship where there is an expectation of trust, which causes harm or distress to an older person or violates their human and civil rights." (Report of the Working Group on Elder Abuse, September 2002)
The age beyond which abuse can be considered elder abuse, is generally 65.
What forms can elder abuse take?
Psychological Abuse:
Can include emotional abuse, threats of harm or abandonment, deprivation of contact, humiliation, blaming, controlling, intimidation, coercion, harassment, verbal abuse, isolation or withdrawal from services or supportive networks.
Financial Abuse:
Often unreported, financial abuse can include theft; fraud; exploitation; pressure in connection with wills, property or inheritance, or financial transactions; or the misuse or misappropriation of property, possessions or benefits.
Physical Abuse:
Forms of elder physical abuse can include slapping, pushing, hitting, kicking, misuse of medication, inappropriate restraint (including physical and chemical restraint) or sanctions.
Neglect:
Sometimes Elder Abuse can involve simple neglect - ignoring medical or physical needs and withholding life necessities, such as medication, adequate nutrition and heating.
Sexual Abuse:
One of the most distressing forms; elder sexual abuse can include rape and sexual assault or acts to which the older adult has not consented, or could not consent, or with which he or she was compelled to consent.
Institutional Abuse:
Elder abuse isn’t confined just to the home. It may include poor care standards in institutions – a lack of positive responses to complex needs, rigid routines, inadequate staffing, and poor staff knowledge of patients or their needs.
How big is the problem?
According to a report on the ‘Abuse and Neglect of Older People in Ireland’* more than 10,000 people over the age of 65 experience mistreatment in a 12-month period in the Republic of Ireland.
A report by the HSE found that in 2014, the reported cases of elder abuse could be broken down as follows…^
• Psychological abuse - 29%
• Financial abuse - 21%
• Self-neglect - 21%
• Neglect - 15%
• Physical abuse - 12%
• Sexual abuse - 1%
• Discrimination - 1%
“Over 10,000 people over 65 in Ireland, experience abuse and neglect in a 12-month period” *
A Red C poll in 2016 found that…
• Physical abuse of vulnerable adults has been witnessed/suspected by 1 in 3 adults.
• Over 1 in 3 of those surveyed has experienced or someone close to them has experienced emotional abuse.
• There is significant public concern about the need to safeguard those who are limited in their ability to protect themselves.
• There is a lack of clarity over where to report vulnerable adult maltreatment, particularly among the young. *^
* National Centre for the Protection of Older People, Abuse and Neglect of Older People in Ireland (2010),
^ HSE Elder Abuse Service report 2014
*^National Safeguarding Committee 2016 Red C poll
Who are the abusers?
A wide range of people may abuse older people. These include relatives and family members, professional staff, paid care workers, volunteers, other service users, neighbours, friends and associates.
The 2014 ‘Open Your Eyes’ report found that of the alleged abusers:
49% were adult children.
19% were a partner/ husband or wife.
15% were an ‘other’ relative.
8% were a neighbour/friend.
5% were related to landlord/lodger.
4% were carers/staff.”
How to spot the signs of elder abuse:
How to recognise if an Older Person is being abused?
Thankfully, most older people do not experience abuse. However, an older person can be harmed or abused in many ways. An older person may also experience more than one form of abuse at any given time. The chart below shows possible indicators of elder abuse.^
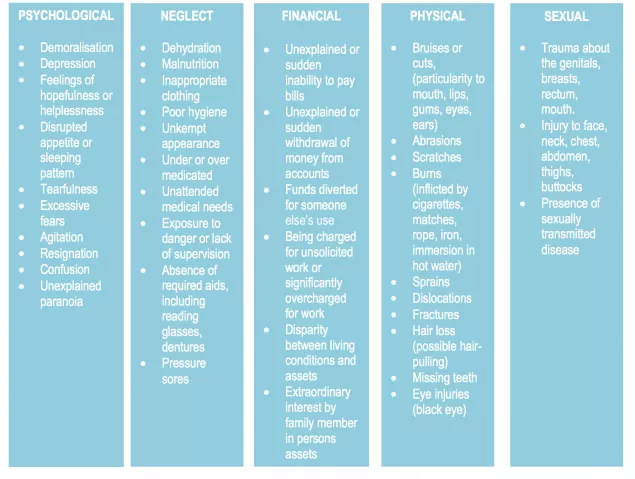
^ Report of the Working Group on Elder Abuse, September (2002)
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SUSPECT SOMEONE IS SUFFERING ELDER ABUSE
So what do you do, if you suspect someone is suffering from elder abuse?
Well, in an emergency, where the person is at immediate risk, you should contact the Gardaí or emergency services on 999 or 112.
If you are concerned about a person you suspect might be a victim of elder abuse, tell someone. You can contact the HSE Elder Abuse Service, your GP, Public Health Nurse, local Health Centre or An Garda Síochána.
The HSE has dedicated Safeguarding and Protection Teams in place all over the country to take reports of elder abuse and provide help.
• For a list of Senior Case Workers in your area and their contact details, click here.
• HSE Information Line - Open Monday to Saturday, 8am-8pm
Call Save: 1850 24 1850
Website: http://www.hse.ie/safeguarding
Email: [email protected]
The Senior Helpline is a national confidential telephone helpline for older people, provided by trained older volunteers. You can also contact the Senior Helpline at the number below:
• LoCall: 1850 440 444 - 7 days a week- 10am –10pm
Website: http://www.thirdageireland.ie/senior-helpline
Email: [email protected]
For a full list of services available to those suffering from elder abuse, click here.
“If we witness domestic violence but choose to walk away; we leave another victim behind. We’re not just bystanders. We’re witnesses.”
Safety
Remember, if you suspect someone is being abused - before you get involved, ask yourself if it’s safe and legal to intervene.
If the situation is already violent or looks like its escalating quickly, don’t directly intervene. Call the Gardaí on 999.
The only effective bystander intervention is a non-violent one.If you see or suspect domestic abuse, visit http://www.whatwouldyoudo.ie or call 999.

Beat 102-103 supporting Cosc #whatwouldyoudo


A message from Cosc and the Dormant Account Fund supported by Beat 102-103.